CFP Optical Transceiver: The Basics
2017-10-09
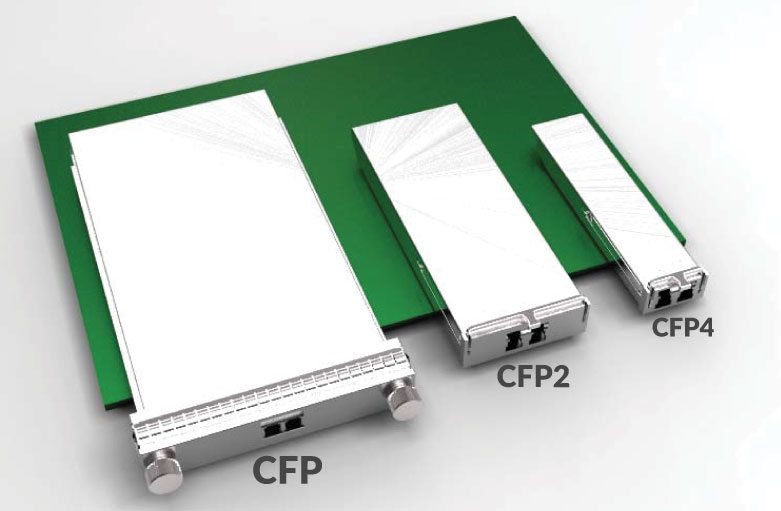
The CFP module is a hot pluggable form factor designed for optical networking applications. CFP is acronym from 100G (C = 100 in Roman numerals; Centum) Form factor Pluggable. As name suggests, CFP is introduced to serve as optical transceiver for 100G interfaces. There are several CFP types introduced – CFP, CFP2 and CFP4, but let’s begin with general CFP architecture. General CFP architecture of CFP divides in two parts – Electrical interface interacting with equipment line card interface and optical line interface.
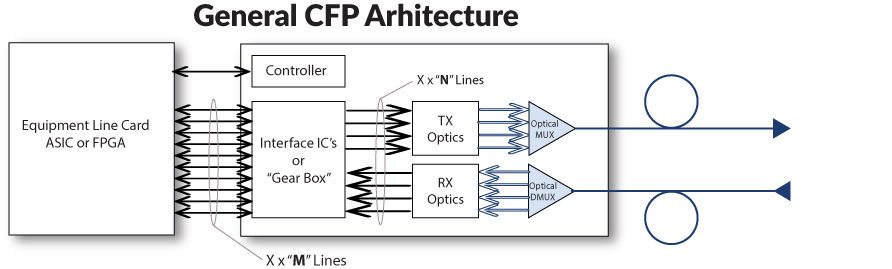
From equipment line card electrical interface aspect CFP has several “M-Lines” with are working 10Gbps speed and separate management interface used for clock & signaling data. If CFP is working 100GBase-LR4 mode, then it has 10 x 10Gbps M-Lines, if 40GBase-LR4 mode, then 4 x 10Gbps M-Lines. So called “Gear Box” is electrical 10:4 Mux/DeMux module aggregating up to 10 M-Line interfaces in maximum 4 N-Line interfaces. In case of 100GBase-LR4 each N-Line speed is 25Gbps and in case of 40GBase-LR4 N-Line speed is 10Gbps. Each N-Line is converted to optical signal with different wavelength and all four wavelengths are transmitted to CFP line interface using built in passive optical multiplexers.
CFP form factor is oldest from CFP family and it has current MSA (Multi Source Agreement) Rev 1.4. It can support both – 100GBase-X and 40GBase-X, and it’s general principle is following:
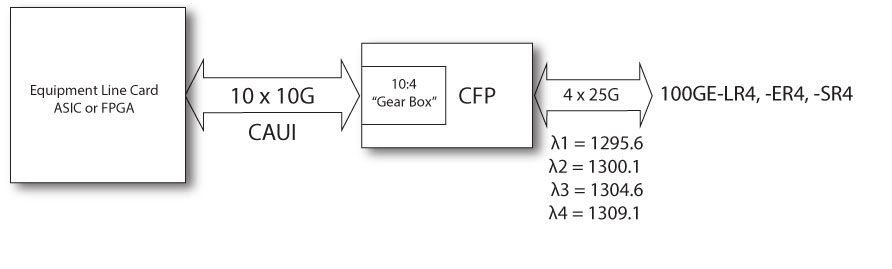
CFP electrical interface for 100G transmission is called CAUI – C (it again represents Roman Centum for 100G) Attachment Unit Interface. CAUI interface was standardized by IEEE802.3ba – Annex 83A, defining that CAUI interface is a parallel electrical interface with each lane running at a nominal rate of 10.3125 Gbps.
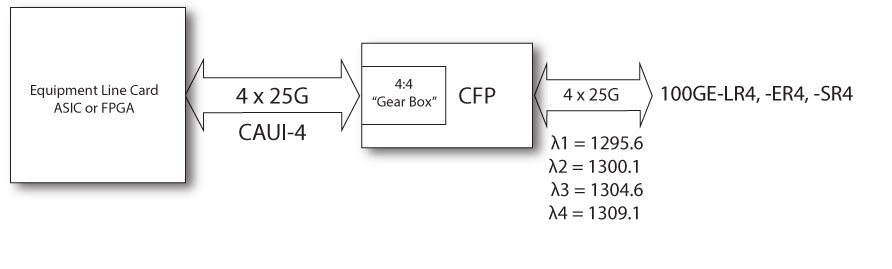
On February 16, 2015, the 802.3bm standard was approved. The 802.3bm standard specifies four-lane chip-to-module and chip-to-chip electrical specification (CAUI-4). In new version of CAUI-4 interface are 4 M-Lines, each running speeds 25.78 Gbps for 100G Ethernet and 27.95 Gbps for SONET/SDH OTU4.
Popular 100G Port implementations using CFP Modules:
100GBASE-SR10 – IEEE Standardized CFP Module using special MPO interface/cable with ten parallel optical fiber pairs (MTP24), each running at 10.31 Gbps and using 850nm lasers. It’s possible to achieve up to 150m.
100GBASE-SR4 – CFP Module using special MPO interface/cable with four parallel optical fiber pairs (MTP12), each running at 25.78 Gbps and using 850nm lasers. It’s possible to achieve up to 150m.
100GBASE-LR4 – IEEE Standardized CFP Module using standard LC dual fiber interface with single mode cable, but running four optical wavelengths each direction (1295.56 nm, 1300.05 nm,1304.59 nm, 1309.14 nm) and muxing/demuxing of these wavelengths happening inside CFP module. Each wavelength is running at 25.78 Gbps and it is possible to achieve up to 10 km. Such formations of four wavelengths sometimes is referred also as LAN-WDM.
100GBASE-ER4 – IEEE Standardized CFP Module using standard LC dual fiber interface with single mode cable, but running four optical wavelengths each direction (1295.56 nm, 1300.05 nm,1304.59 nm, 1309.14 nm) and muxing/demuxing of these wavelengths happening inside CFP module. Each wavelength is running at 25.78 Gbps and it’s possible to achieve up to 40 km.
100GBASE-ZR – Proprietary standard (Juniper for example) CFP Module using standard LC dual fiber interface with single mode cable, but running 193.90 THz (+/-1.8 GHz) / 1546.119 nm DWDM wavelength with Dual polarization-quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK) with forward error correction (FEC), or other words it’s Coherent Optics transmission. Each phase-shifted/polarized wavelength is running at 25.78 Gbps and it’s possible to achieve up to 80 km.
This is basic introduction of CFP first generation optical transceivers, and in some future posts we will try to cover CFP2 and CFP4 form factors and their implementations.
RECENT BLOG POST
-
012019-10With the continuous development of 5G communication technology, 100G modules are gradually becoming popular. We know that there are many kinds of packages for 100G optical modules. From 2000 to now, the optical module package types have been rapidly developed. Its main package types are: GBIC, SFP, XENPAK, SNAP12, X2, XFP, SFP+, QSFP/QSFP+, CFP, CXP. In the fast-developing network era, some 100G optical modules avoid the risk of being eliminated, and upgraded and revised with the wave of the Internet, such as 100G CFP optical modules.
-
012019-101. What is the CWDM SFP? The CWDM optical module is an optical module using CWDM technology to implement the connection between the existing network device and the CWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer. When used with a CWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer, CWDM optical modules can increase network capacity by transmitting multiple data channels with separate optical wavelengths (1270 nm to 1610 nm) on the same single fiber.
-
012019-10AOC is the abbreviation of Active Optical Cables, which is called Active Optical Cables in Chinese. AOC active optical is to encapsulate two optical modules and cable together. Because the medium of transmission in the middle is optical cable, AOC optical module, which contains laser devices, has a higher price for DAC. However, its optical aperture is not exposed, it has high reliability, and its working distance can be customized for a long distance of less than 100 meters.
-
012019-10Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) technology is capable of transmitting data in an optical fiber using bit wavelength parallel transmission or string line transmission using the wavelength of the laser.It is widely used in different fields of communication networks, including long-distance backbone networks, metropolitan area networks (MANs), residential access networks, and local area networks (LANs).The DWDM optical module is the optical module that uses this technology, so the DWDM optical module has high bandwidth and long-distance transmission characteristics.